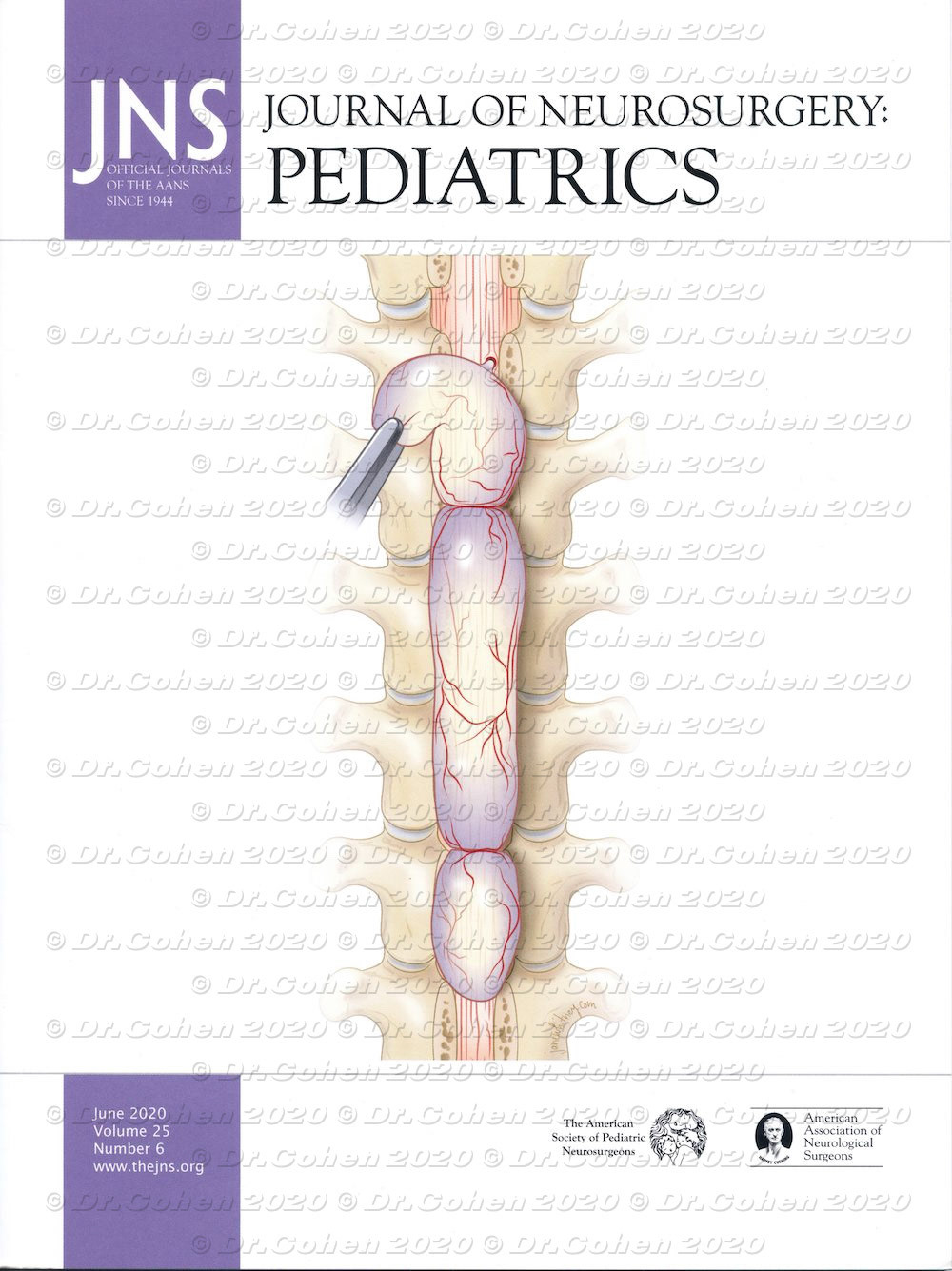
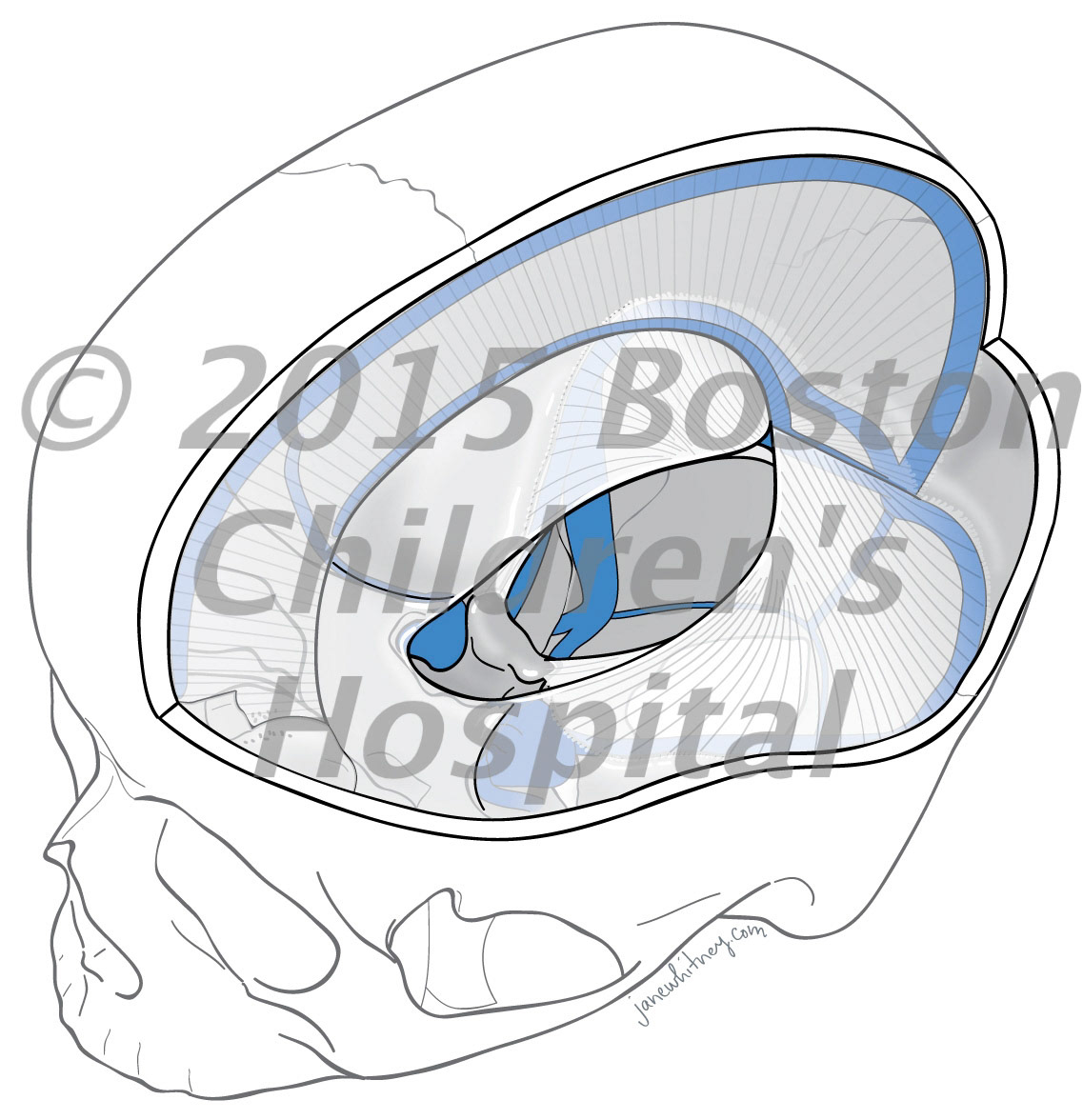
Spinal extradural arachnoid cysts (SEACs) are uncommon spinal lesions that may cause myelopathy, most frequently in the 2nd decade of life. Three contiguous but separate spinal cysts were identified intraoperatively, and they were completely excised with closure of the dural defects. The patient recovered motor and sensory function of the lower extremities. Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics, 2020, cover https://doi.org/10.3171/2019.12.PEDS19108

JNS Pediatrics cover 2021, chiari malformation

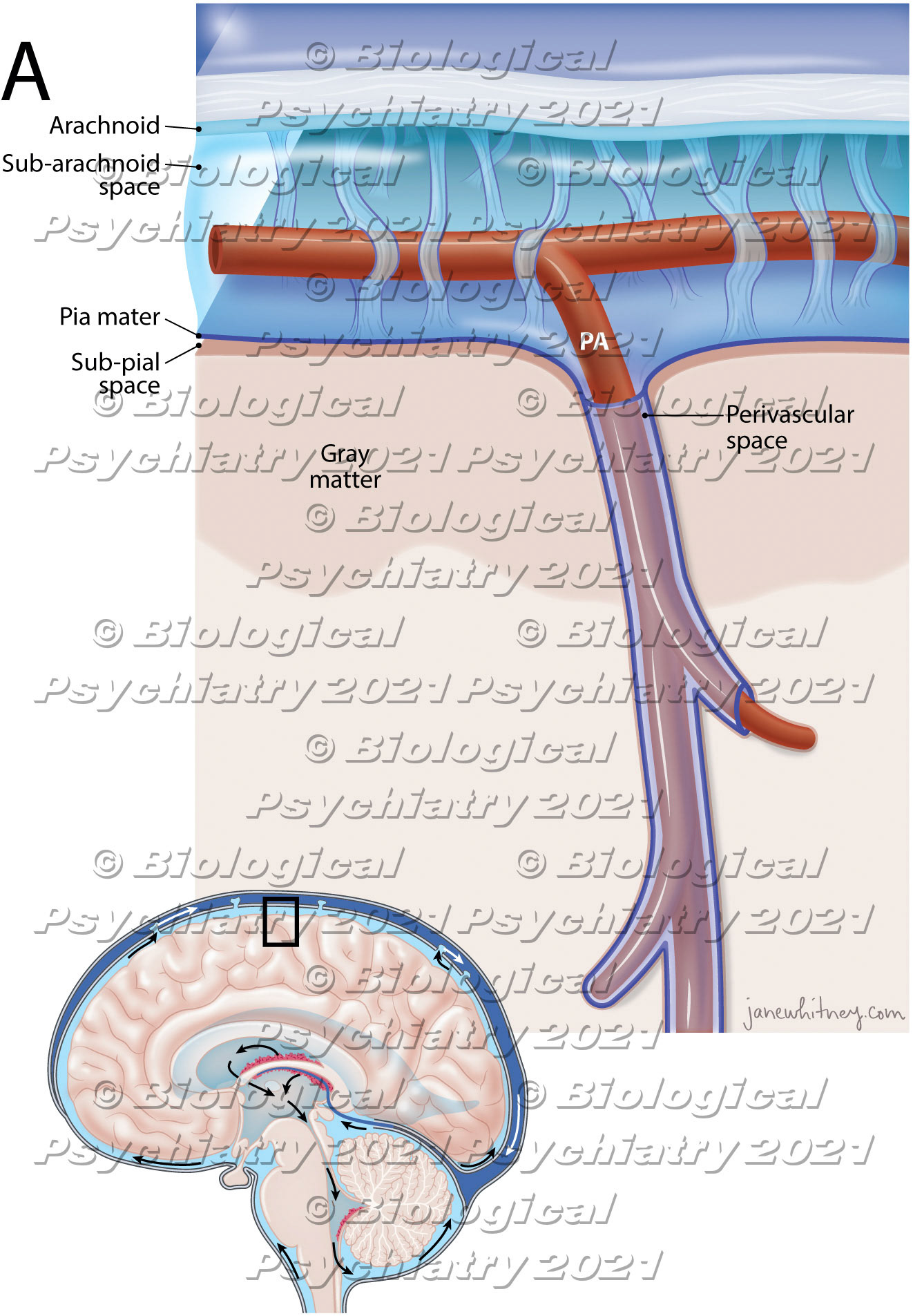
Perivascular spaces, also known as Virchow-Robin spaces are fluid-filled spaces in the brain that surrounds small arterioles, capillaries and venules in the brain.Biological Psychiatry https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2021.06.025

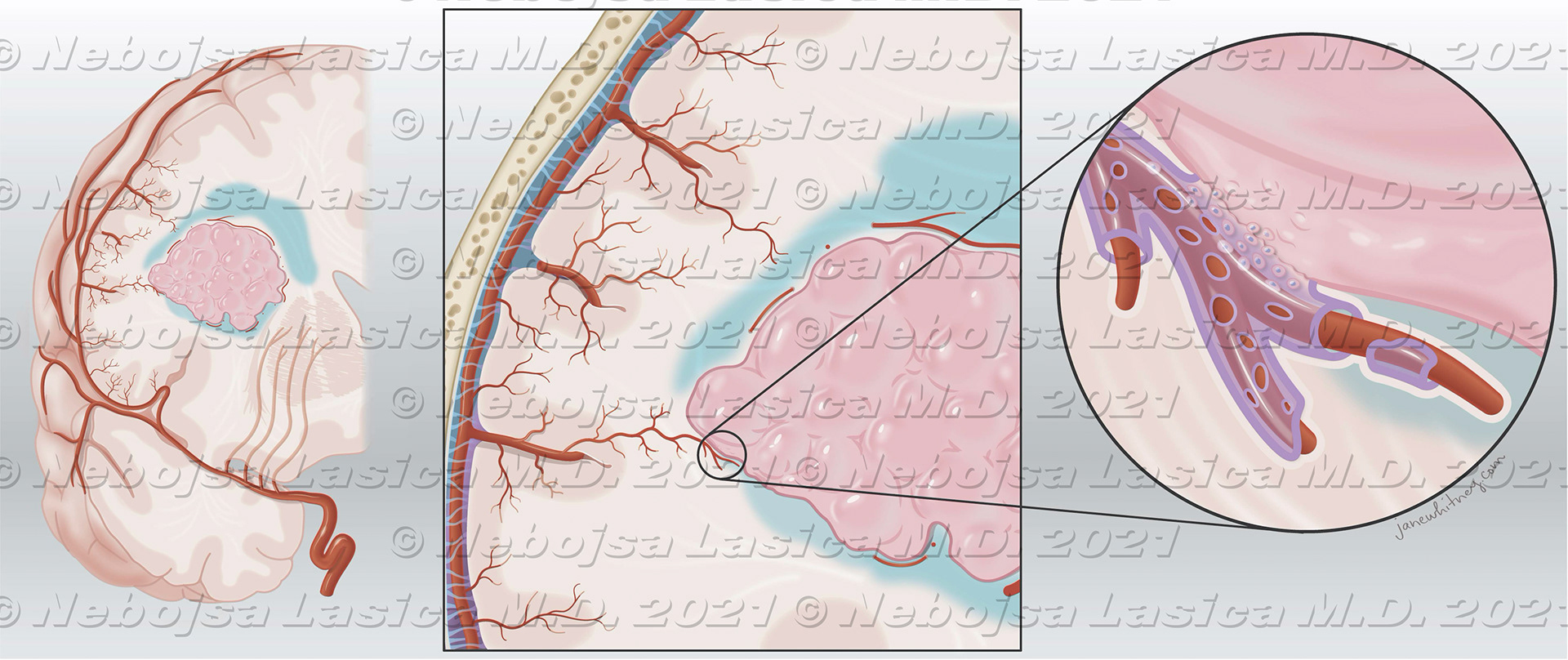
The primary intraparenchymal meningioma of thefrontal lobe (A) with no apparent dural attachment. Thepresumption is that arachnoid cells present in the pia matermigrate together with penetrating blood vessels duringbrain development (B).World Neurosurgery, Sept. 2021https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2021.06.139

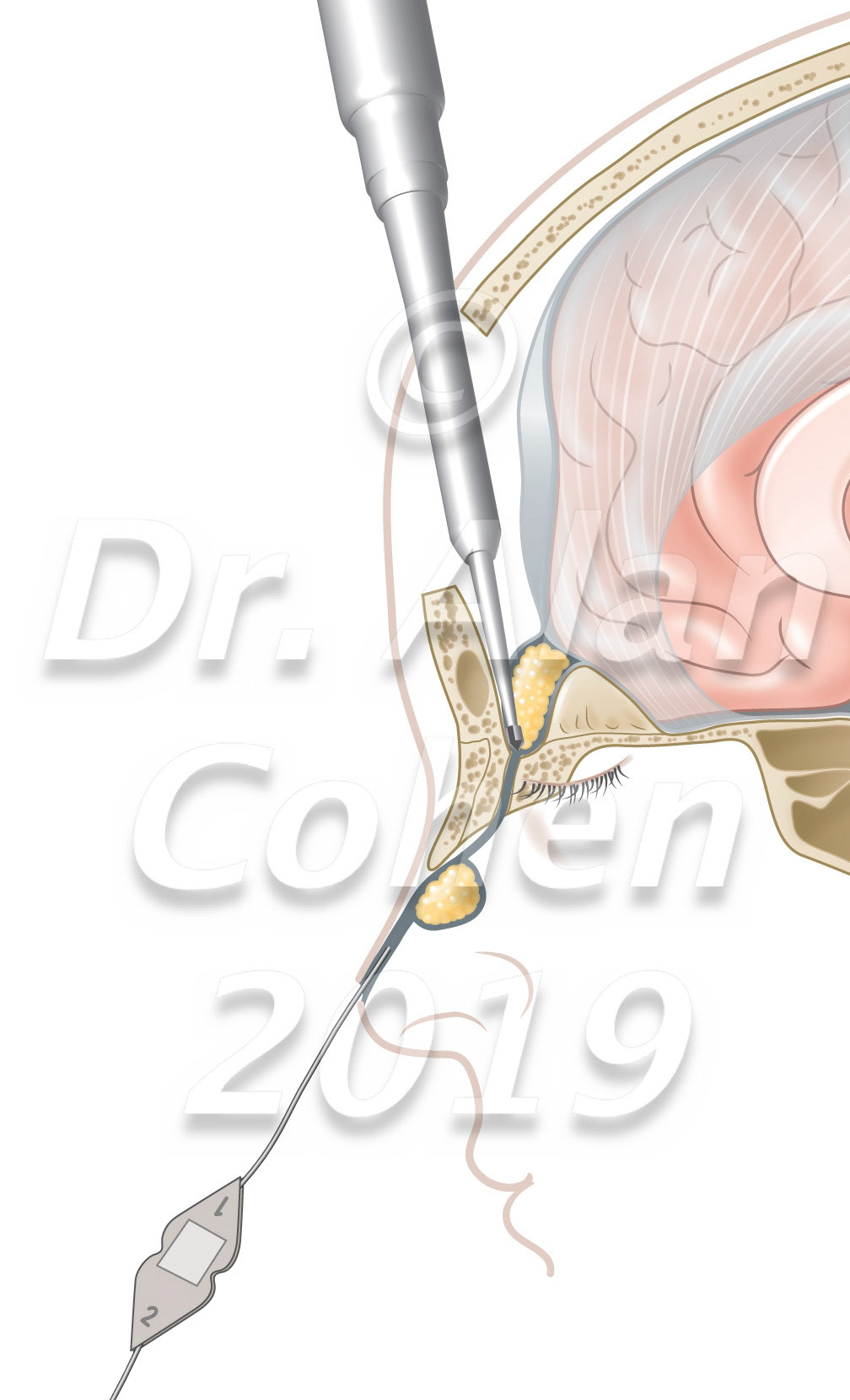
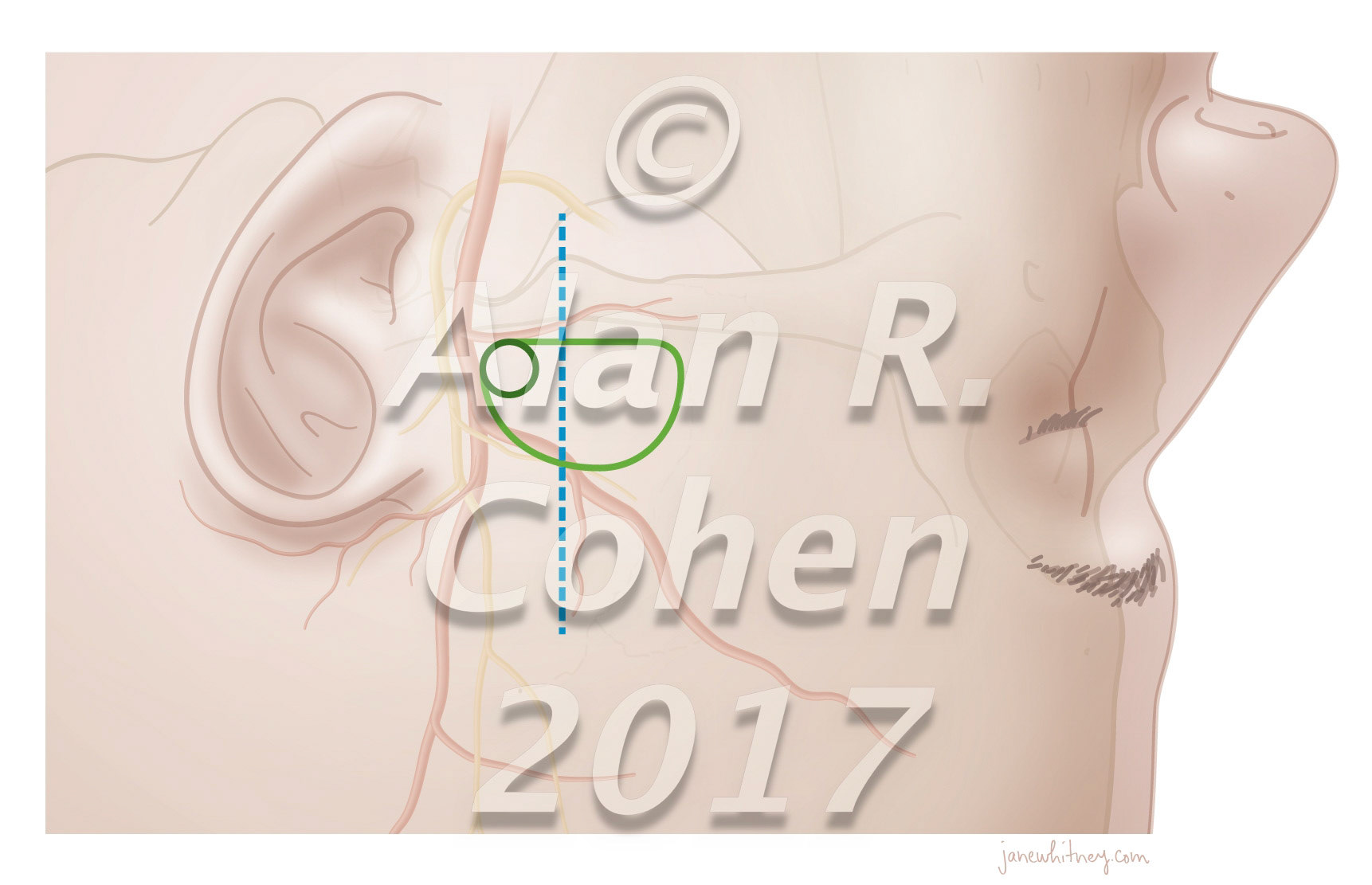
Meet in the middle technique. The neurosurgeon removes the intracranial cyst and sinus tract working through a small bifrontal craniotomy and drilling through the foramen cecum. The plastic surgeon excises the nasal punctum and uses an external rhinoplasty to remove the extracranial lesion. Child's Nervous System, 2020 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04499-5

Tentorium

Pneumorrhachis: The most frequent initial mechanism is an increase in intraalveolar pressure (acute asthma, recurrent vomiting, or closed thoracic trauma). Barotrauma and alveolar rupture allow air migration along the bronchial tree up to the mediastinum. The collected air then separates the mediastinal pleura from the aorta and the parietal pleura from the spine; therefore, it enters the epidural space via the intervertebral foramina. The suddenness, more than the size of the pneumothorax, induces this initial increase in intra-alveolar pressure. Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine Oct 2020 https://doi.org/10.3171/2020.6.SPINE20648

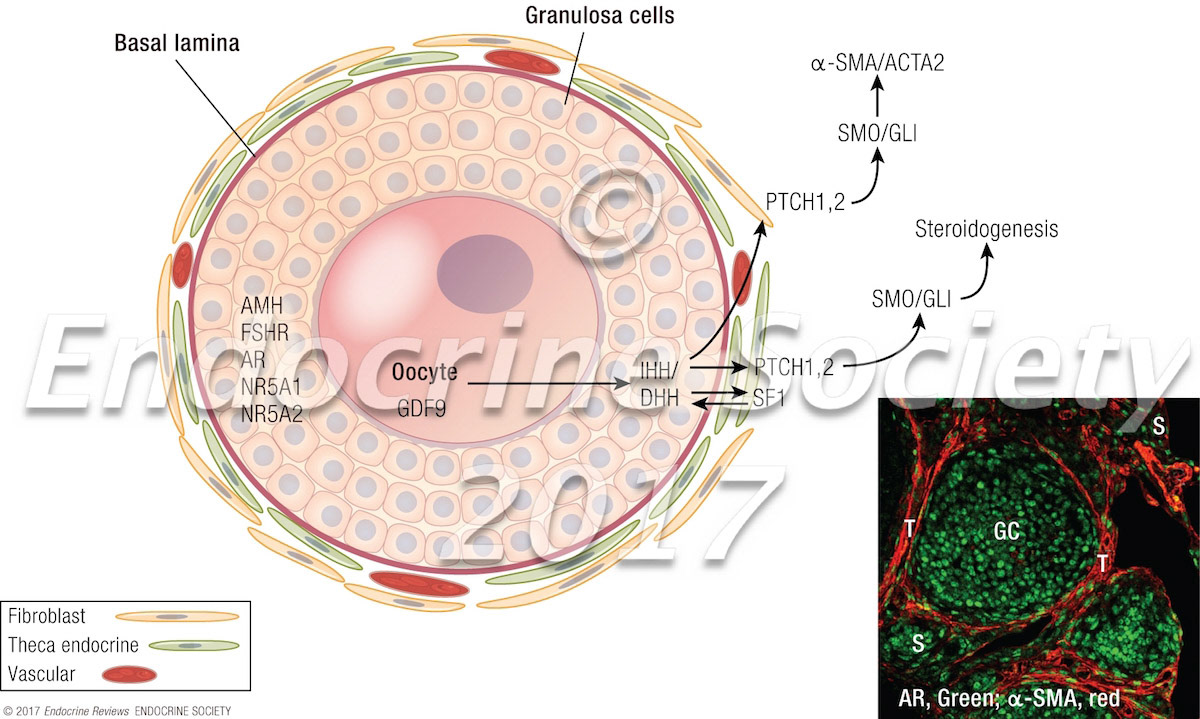
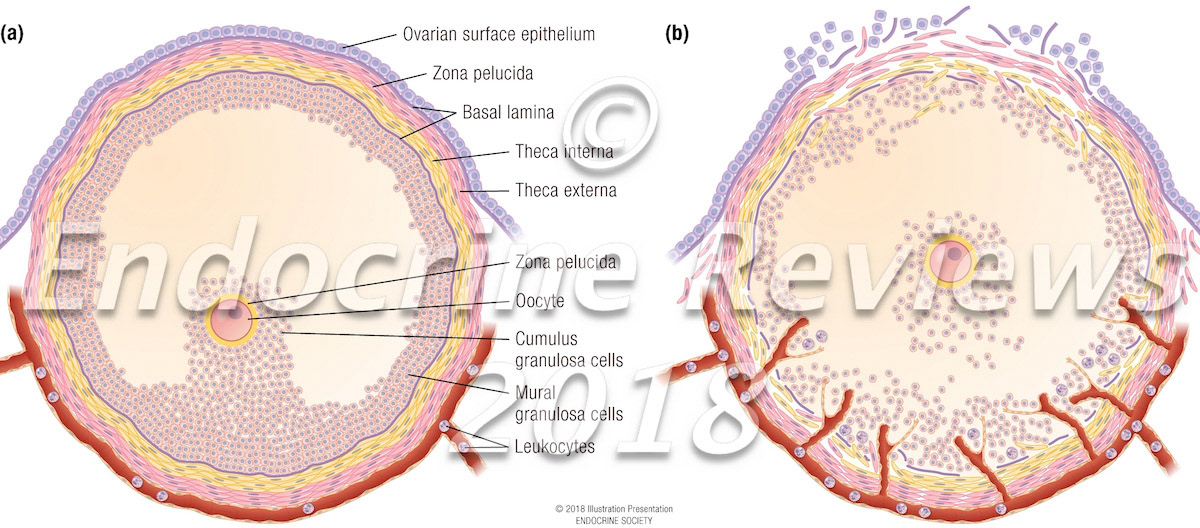
Establishment of the theca cell layer

Medtronic 723 pump

Omnipod Horizon automated insulin delivery and PDM app on smartphone

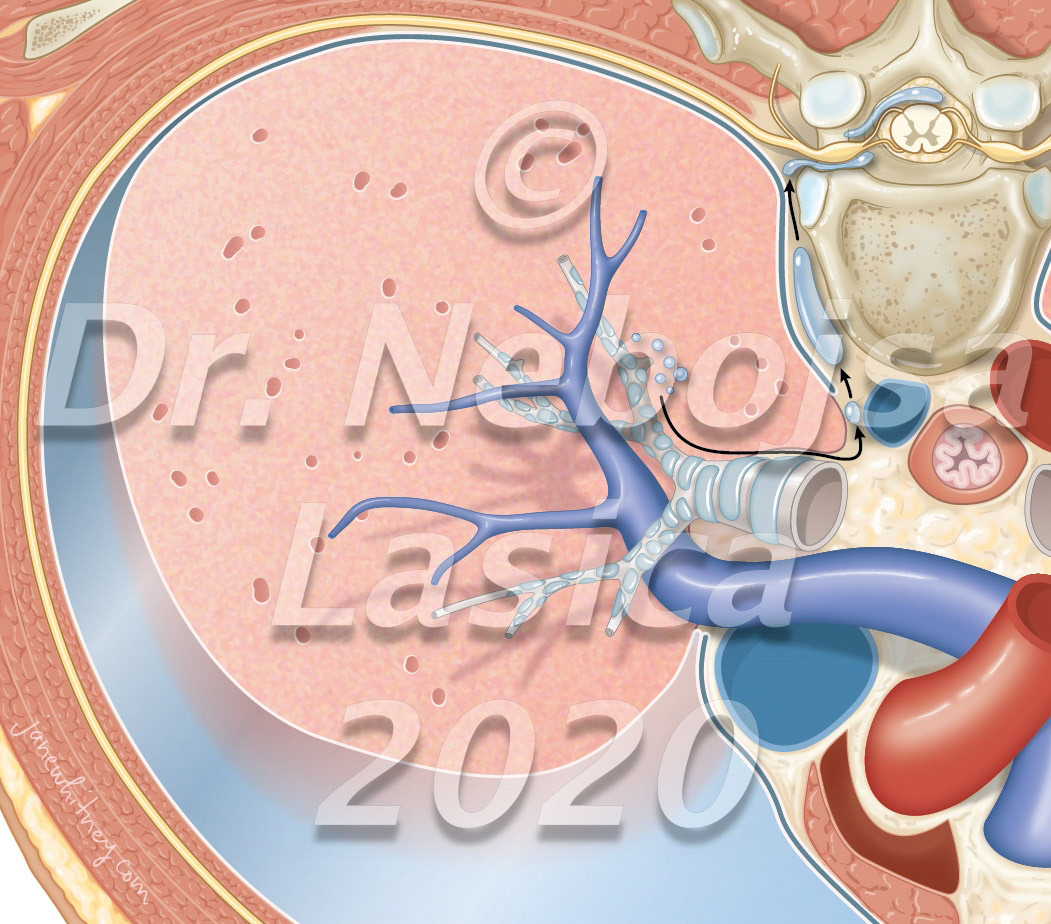
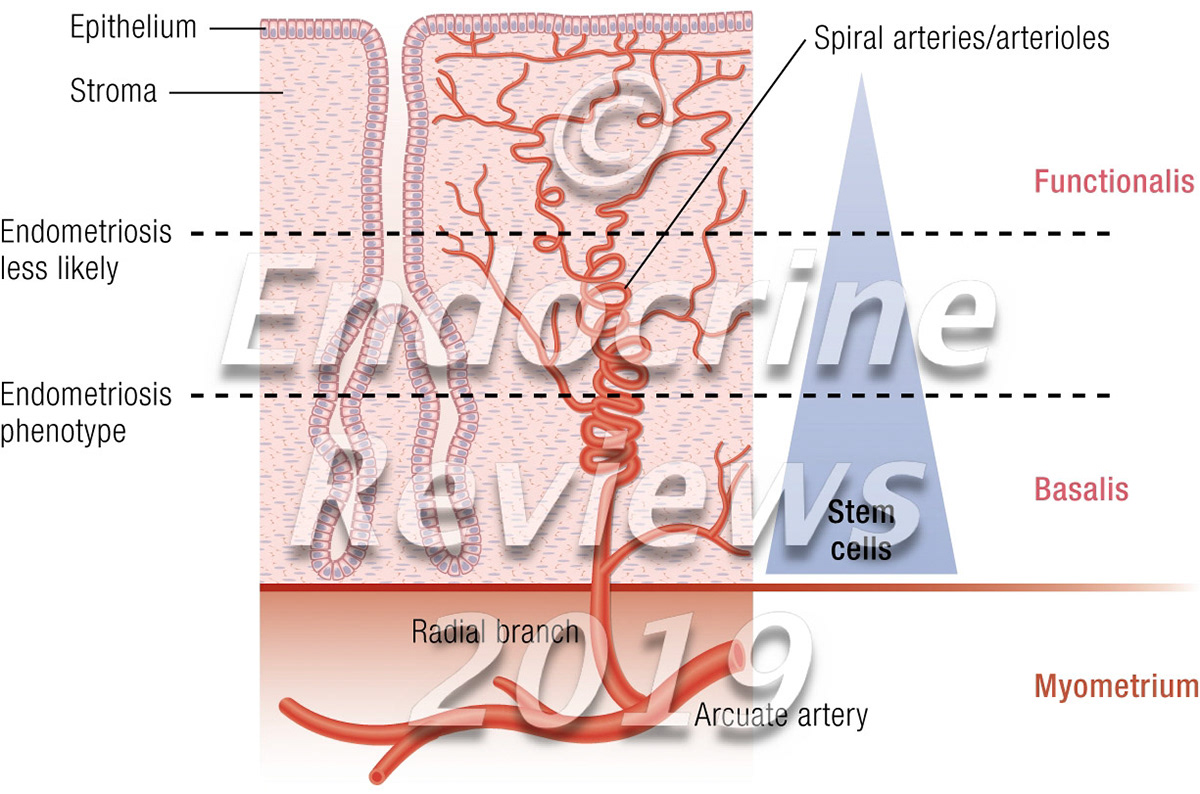
Endometrium

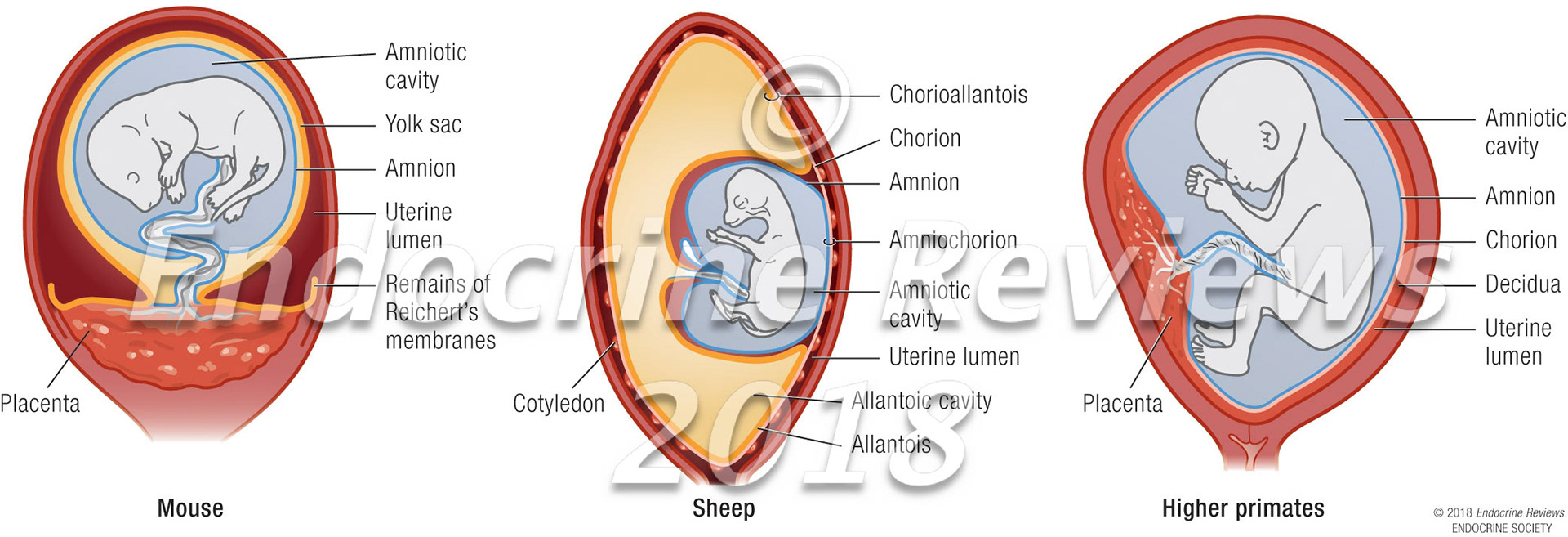
Membranes and placenta comparison: mouse, sheep, human

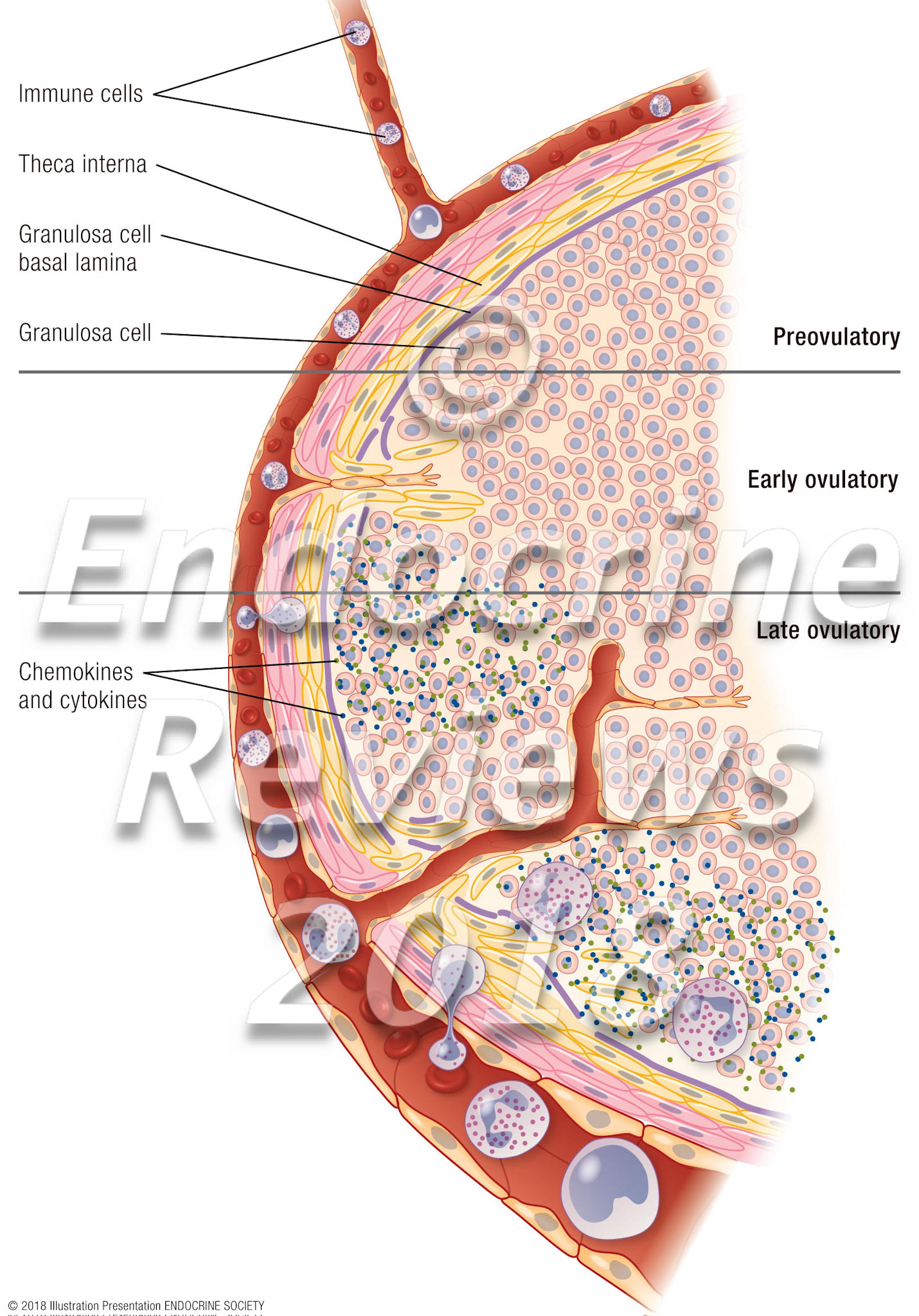
Preovulatory follicle

Ovulatory follicle: Capillary growth

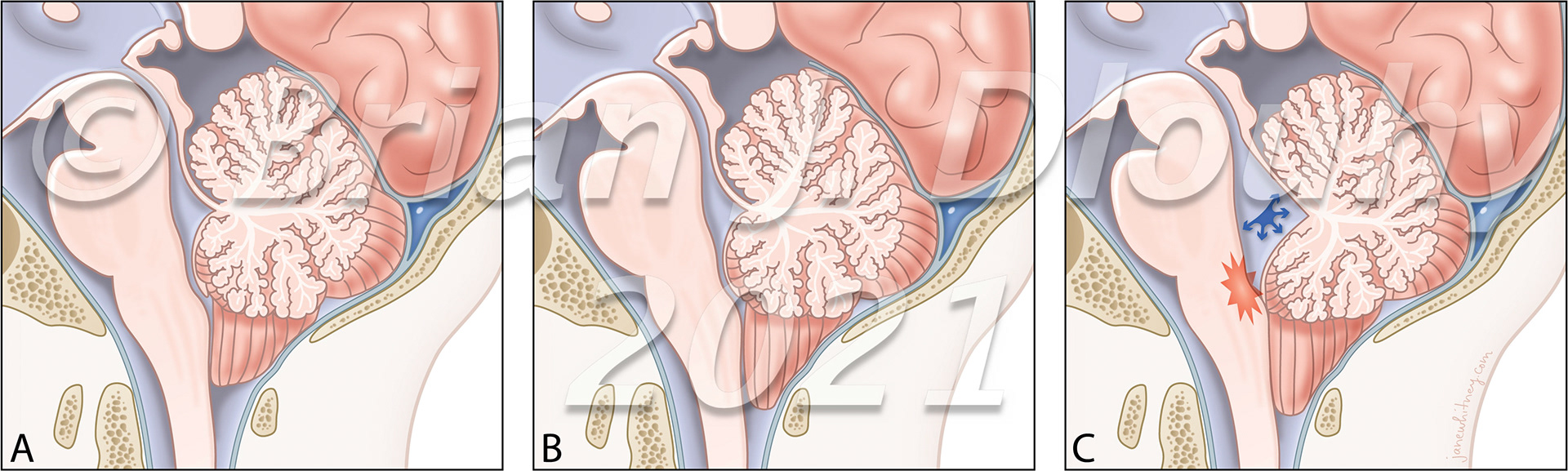
ER 2018-00017_Fig 1+k+j2

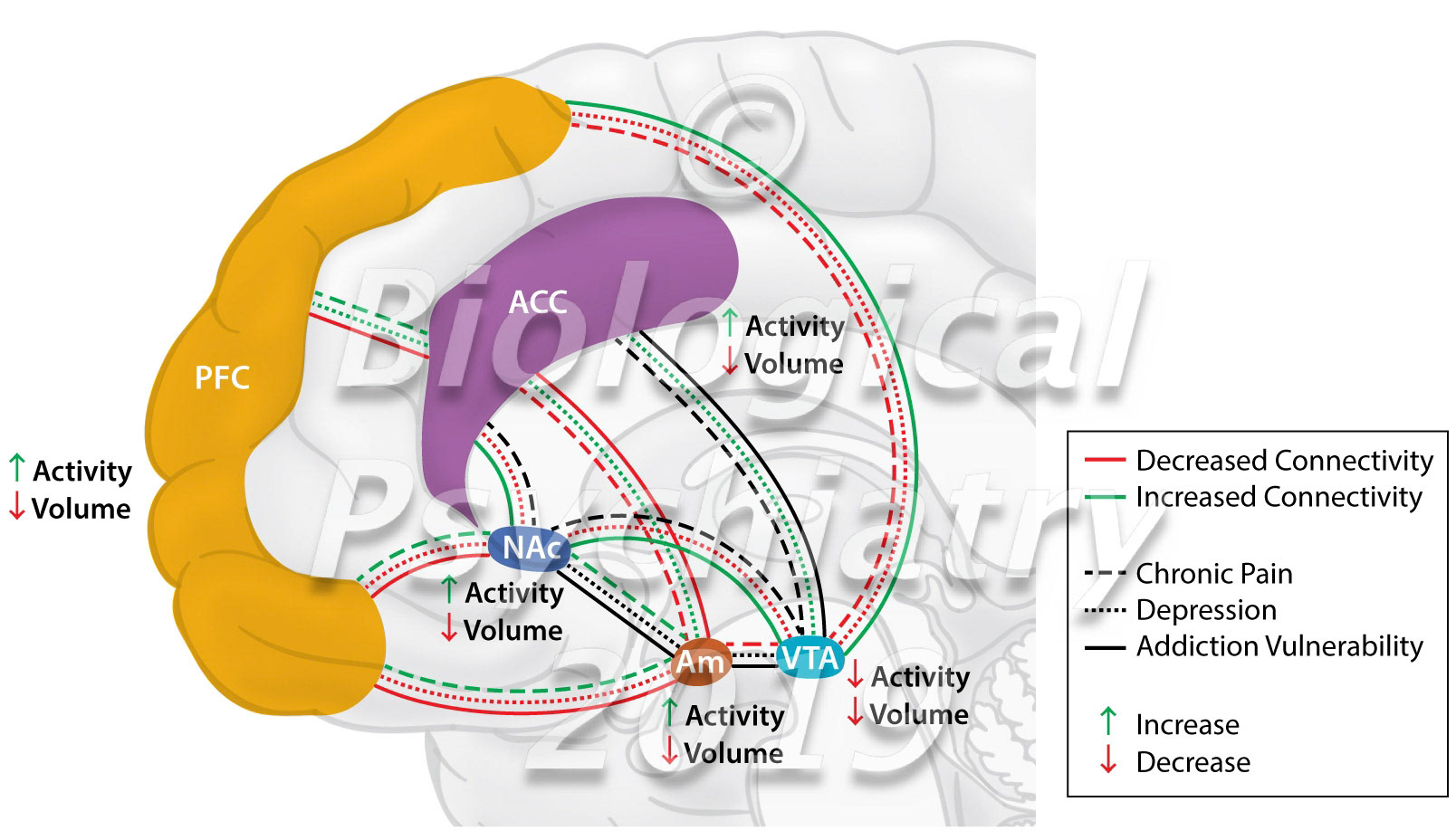
The Mesolimbic Dopamine System in Chronic Pain and Associated Affective Comorbidities Biological Psychiatry https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.10.018

Imaris Snapshot

Mouse brain, midsagittal

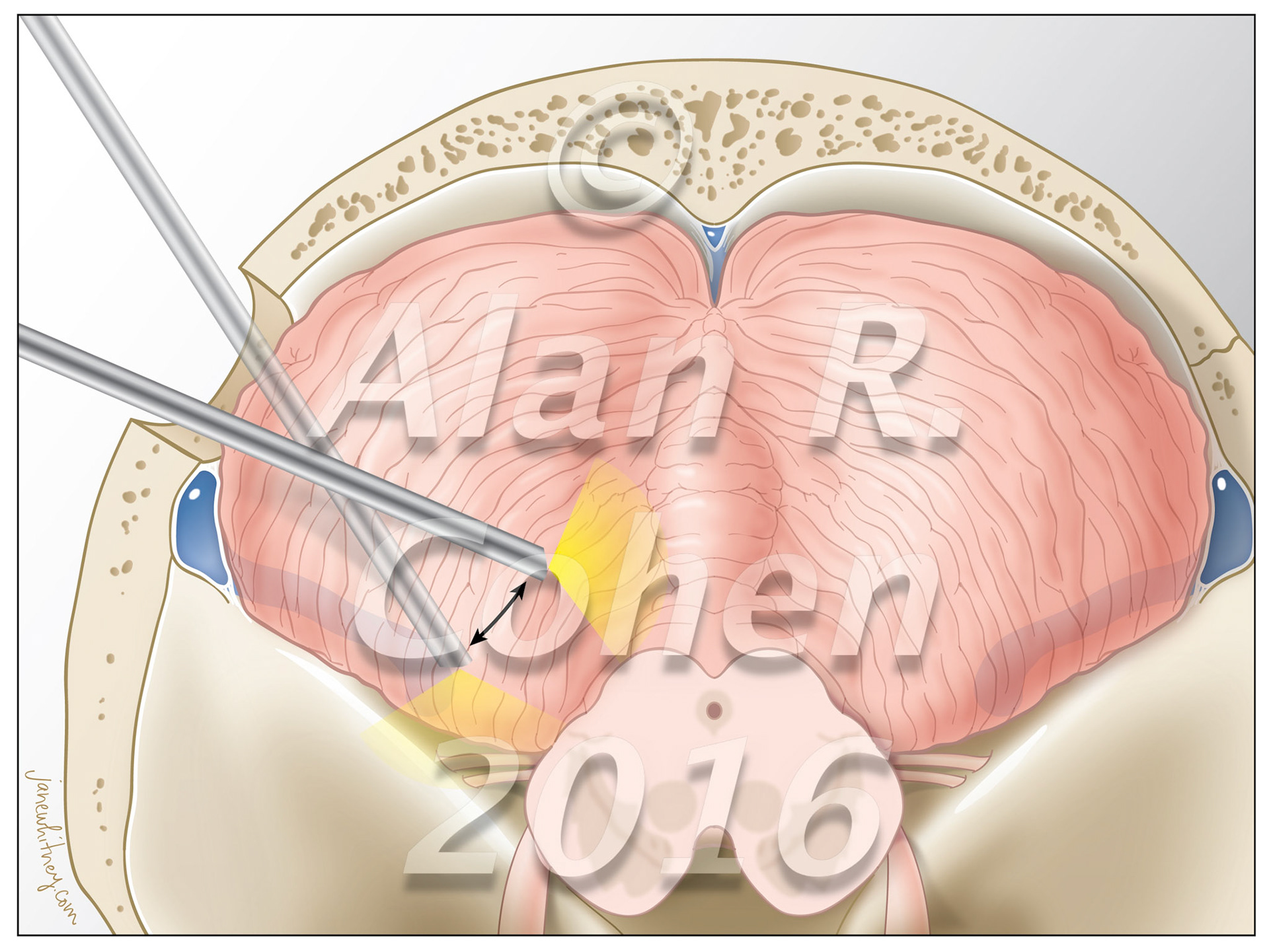
Despite recent technological advances, direct approaches to the posterolateral incisural space remain surgical challenges. The extreme lateral infratentorial supracerebellar approach to treat pathologies located in the ambient cistern and posterior incisural space is a technically feasible route in selected cases. World Neurosurgery, July 2016 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.04.017

Endoscope-Assisted Microsurgical Subtemporal Keyhole Approach to the Posterolateral Suprasellar Region and Basal Cisterns World Neurosurgery July 2017 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.02.054

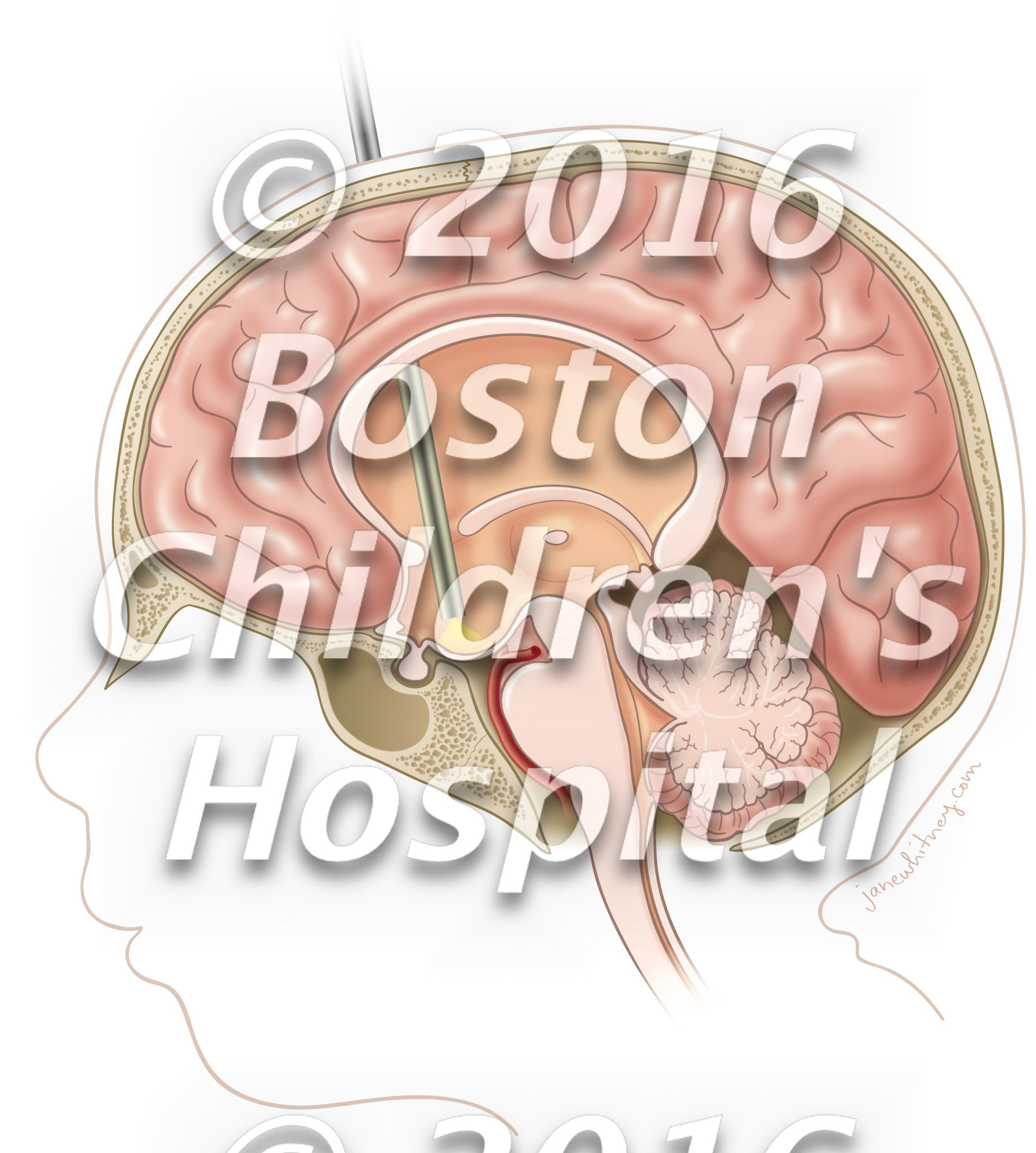
Figure_1_ETV_draft9

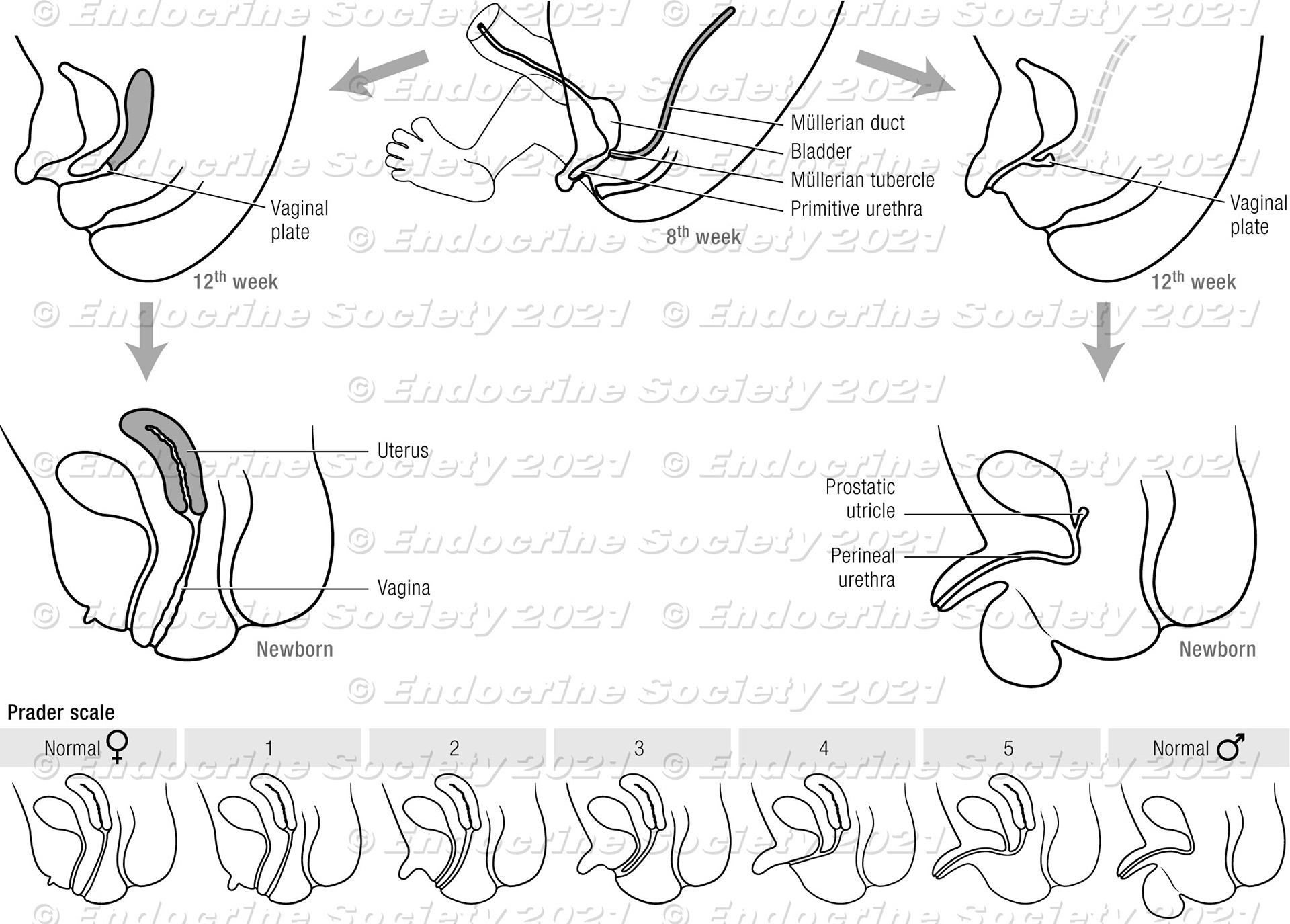
Genital development. Top, Differentiation of male and female reproductive systems are illustrated in schematic cross-section (not to scale). Bottom, the Prader scale of genital virilization.

Fourth ventricle roof angle as a measure of fourth ventricle bowing and a radiographic predictor of brainstem dysfunction in Chiari malformation type I Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics Sept. 2021